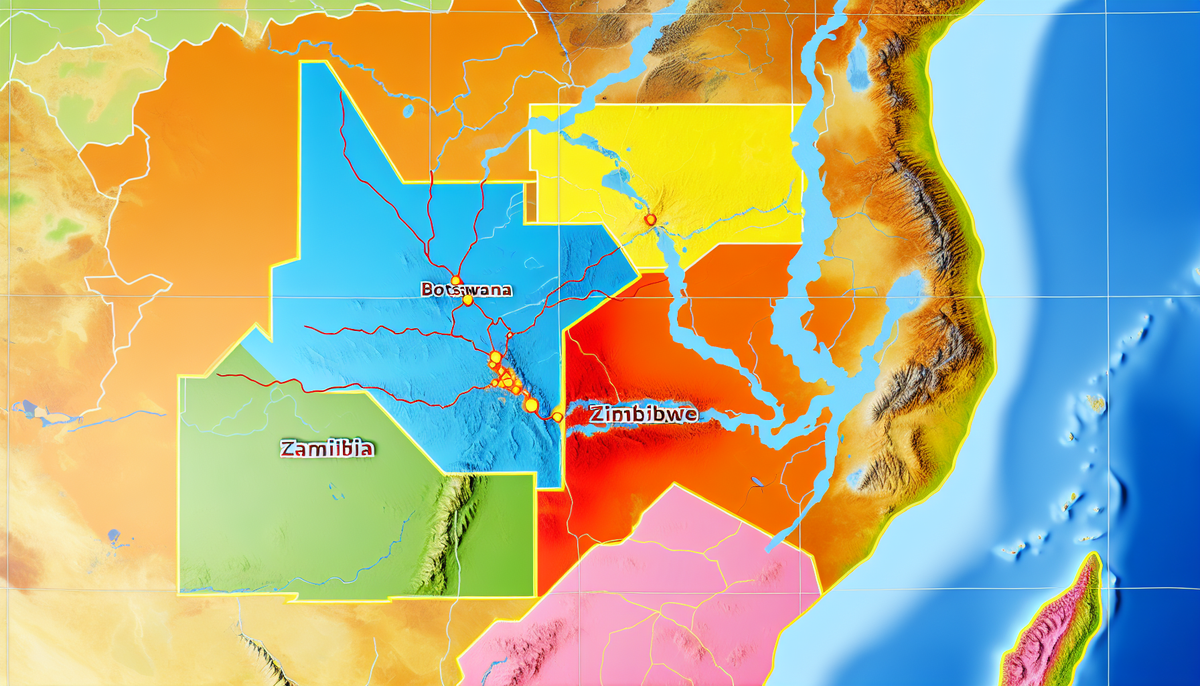
Where the borders of Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe meet
Origin and Significance of the Quadripoint Junction
The quadripoint junction where Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe converge is a unique geographical feature with both historical and contemporary significance. This point, known as the "Four Corners," is not just a curiosity; it symbolizes the intersection of diverse cultures, languages, and traditions. The origin of the quadripoint dates back to colonial times when borders were arbitrarily drawn, often without consideration for the local populations and their ways of life. This historical context adds a layer of complexity to the current dynamics in the region.
The significance of this junction extends beyond its geographical curiosity. The meeting point serves as a critical economic hub for trade and travel, facilitating cross-border commerce and interaction among the neighboring nations. Moreover, it attracts tourists eager to experience standing in four countries simultaneously, enriching the local economy and promoting cultural exchange.
Environmental factors also play a vital role in this area, given its rich biodiversity and natural resources. As countries grapple with conservation issues and sustainable practices, the quadripoint serves as a focal point for collaborative efforts to protect the environment while fostering community relationships. Overall, the quadripoint is a microcosm of the complexities and intersections that define southern Africa today.
Ecological Diversity Across Four National Borders
The quadripoint junction of Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe is a remarkable intersection of ecological diversity. Each of these nations boasts unique ecosystems that contribute to a rich tapestry of wildlife and natural habitats. Botswana is home to the expansive Okavango Delta, a UNESCO World Heritage site characterized by intricate waterways teeming with fauna. To the south, Namibia showcases the stunning Namib Desert, featuring unique adaptations of flora and fauna that thrive in arid conditions.
Zambia is renowned for its vast national parks, including South Luangwa, which offers some of Africa's best wildlife viewing opportunities, while Zimbabwe's Hwange National Park is famous for its large elephant population. The convergence of these diverse ecosystems promotes a variety of habitats, from wetlands to grasslands and forests, fostering interdependent relationships among species.
The quadripoint area also plays a crucial role in cross-border conservation efforts. Collaborative initiatives, such as transfrontier conservation areas, aim to preserve the ecological integrity of these regions. These efforts not only benefit wildlife but also enhance biodiversity and ecosystem resilience in the face of climate change. Ultimately, the ecological diversity around the quadripoint illustrates the interconnectedness of nature and the importance of cooperative stewardship of these precious resources.
Economic Impacts and Trade at the Intersection
The quadripoint junction of Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe serves as a significant economic crossroads, facilitating trade and commerce among the four nations. This unique geographical feature promotes cross-border trade routes, making it an advantageous position for businesses looking to capitalize on the diverse markets available. Local economies benefit from the easy movement of goods and services, which enhances regional prosperity.
Markets at the quadripoint support a range of industries, including agriculture, mining, and tourism. Local farmers engage in trade, selling agricultural products such as grains and vegetables across borders, boosting food security and livelihoods. Similarly, mining operations, particularly in Zambia and Zimbabwe, affect regional commerce, as minerals are transported to Botswana and Namibia for processing and export.
Tourism also plays a pivotal role in the economic landscape of this region. Visitors flock to experience the rare opportunity of standing in four countries at once. This influx of tourists generates revenue for local businesses, from hotels to craft markets, creating jobs and fostering community development.
Additionally, cooperative trade agreements among these nations enhance economic relationships, promoting sustainable practices and ensuring mutual benefits. The quadripoint thus stands as a vital economic hub, reflecting the potential for collaborative growth in southern Africa.
Cultural Interchange in the Quadripoint Area
The quadripoint junction where Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe meet is a vibrant tapestry of cultural interchange. This unique geographical location fosters interaction among diverse ethnic groups, including the Tswana, Herero, Lozi, and Shona. Each group brings its own rich traditions, languages, and customs, creating a dynamic cultural landscape that is continuously evolving.
Festivals and communal events often see participation from neighboring communities, showcasing traditional music, dance, and cuisine. Events like the Zambezi Festival celebrate the cultural heritage of all four countries, encouraging unity and appreciation of each other's customs. This cultural exchange not only promotes mutual respect but also enriches the identities of the people living in the region.
Furthermore, the blending of cultures is evident in the local markets where artisans and craftsmen sell their work, reflecting a fusion of styles and techniques from each nation. Cushions, pottery, and jewelry often embody features that speak to the intersecting influences of the different cultures.
In educational contexts, initiatives encouraging cross-border collaboration provide opportunities for students to learn about one another’s histories and traditions. Through storytelling and shared experiences, the quadripoint area thrives as a symbol of cultural unity, offering enriching experiences for both residents and visitors alike.
Tourism and the Allure of a Multi-National Corner
The quadripoint junction where Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe meet is an alluring destination for tourists seeking unique experiences. This multi-national corner offers visitors the rare opportunity to stand in four countries at once, drawing adventurous souls from around the globe. The novelty of crossing borders so seamlessly adds an intriguing layer of excitement to any trip.
Tourism infrastructure around the quadripoint has developed to cater to this growing interest, with a range of activities available for visitors. From wildlife safaris in Botswana's Okavango Delta to exploring the dramatic landscapes of Namibia’s deserts and Zimbabwe’s stunning Victoria Falls, tourists can immerse themselves in the breathtaking beauty of southern Africa. Each neighboring country offers distinct attractions, creating a rich tourism experience in one concentrated area.
Cultural exchanges enhance the appeal, as visitors can interact with diverse communities, learn about traditional crafts, and enjoy local cuisines. Furthermore, tour operators often offer cross-border experiences, allowing travelers to explore multiple nations in a single journey.
With its captivating natural landscapes, vibrant cultures, and rich history, the quadripoint area has become a magnet for tourists. This region not only boosts the local economies but also fosters cross-cultural understanding, making it a treasured destination for all.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges in the Region
The quadripoint junction of Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe is a rich ecological zone that faces both conservation opportunities and challenges. Collaborative efforts among these nations aim to protect and preserve the region's diverse ecosystems, which include wetlands, savannahs, and forests that are home to numerous endangered species. Transfrontier conservation areas (TFCAs) are a key strategy, allowing for the establishment of protected areas that span national borders, enhancing habitat connectivity and facilitating wildlife migration.
However, the region grapples with significant challenges. Poaching, particularly of elephants and rhinoceroses, remains a persistent threat, driven by demand for ivory and other illegal wildlife products. In addition, habitat loss due to agriculture, mining, and urbanization poses risks to biodiversity. Climate change also exacerbates these challenges, leading to altered rainfall patterns and affecting the delicate balance of local ecosystems.
Community involvement is crucial in conservation efforts, as local populations rely on natural resources for their livelihoods. Initiatives that promote sustainable practices and eco-tourism provide economic incentives for communities to protect their environment. As these countries work together, balancing development with conservation remains a complex but essential task, vital for safeguarding the region’s ecological treasures for future generations.
Infrastructure Development and Cross-Border Cooperation
Infrastructure development in the quadripoint region of Botswana, Namibia, Zambia, and Zimbabwe plays a crucial role in enhancing cross-border cooperation. As the four nations explore opportunities to strengthen their economic ties, investments in transportation, communication, and energy become vital. Improved highways and rail networks facilitate the movement of goods and people, streamlining trade routes and promoting regional integration.
The establishment of border posts equipped with modern facilities accelerates the customs process, allowing for smoother transit across countries. These advancements not only support the local economies but also lay the groundwork for collaborative initiatives, such as joint tourism programs and conservation projects.
Energy cooperation is also on the rise, with initiatives aimed at sharing resources and infrastructure to promote sustainable energy solutions. For example, cross-border power projects can enhance energy security and access, benefiting communities in each nation.
Through joint ventures and partnerships, the countries leverage their unique strengths, fostering collaboration on infrastructure that supports economic growth and development. While challenges remain—such as differing national policies and funding limitations—the emphasis on cross-border cooperation through infrastructure development is essential in realizing a more connected and prosperous southern Africa. This collaboration ultimately enhances resilience and integration in the region.